
An orifice meter is a device used for measuring the rate of fluid flow. It uses the same principle as a Venturi nozzle, namely Bernoulli's principle which says that there is a relationship between the pressure of the fluid and the velocity of the fluid. When the velocity increases, the pressure decreases and vice versa.
An orifice plate is basically a thin plate with a hole in the middle. It is usually placed in a pipe in which fluid flows. As fluid flows through the pipe, it has a certain velocity and a certain pressure. When the fluid reaches the orifice plate, with the hole in the middle, the fluid is forced to converge to go through the small hole; the point of maximum convergence actually occurs shortly downstream of the physical orifice, at the so-called vena contracta point (see drawing to the right). As it does so, the velocity and the pressure changes. Beyond the vena contracta, the fluid expands and the velocity and pressure change once again. By measuring the difference in fluid pressure between the normal pipe section and at the vena contracta, the volumetric and mass flow rates can be obtained from Bernoulli's equation.
By assuming steady-state, incompressible (constant fluid density), inviscid, laminar flow in a horizontal pipe (no change in elevation) with negligible frictional losses, Bernoulli's equation reduces to an equation relating the conservation of energy between two points on the same streamline:

or:

By continuity equation:
 or V1 = Q / A1
and V2 = Q / A2 :
or V1 = Q / A1
and V2 = Q / A2 :

Solving for Q:

and:

The above expression for Q gives the theoretical volume flow rate. Introducing the beta factor β = d2 / d1 as well as the coefficient of discharge Cd:

And finally introducing the meter coefficient C
which is defined as
 to obtain the final equation for the volumetric flow of the fluid through the
orifice:
to obtain the final equation for the volumetric flow of the fluid through the
orifice:

Multiplying by the density of the fluid to obtain the equation for the mass flow rate at any section in the pipe:[1][2][3][4]

| where: | |
| Q | = volumetric flow rate (at any cross-section), m³/s |
|---|---|
 |
= mass flow rate (at any cross-section), kg/s |
| Cd | = coefficient of discharge, dimensionless |
| C | = orifice flow coefficient, dimensionless |
| A1 | = cross-sectional area of the pipe, m² |
| A2 | = cross-sectional area of the orifice hole, m² |
| d1 | = diameter of the pipe, m |
| d2 | = diameter of the orifice hole, m |
| β | = ratio of orifice hole diameter to pipe diameter, dimensionless |
| V1 | = upstream fluid velocity, m/s |
| V2 | = fluid velocity through the orifice hole, m/s |
| P1 | = fluid upstream pressure, Pa with dimensions of kg/(m·s² ) |
| P2 | = fluid downstream pressure, Pa with dimensions of kg/(m·s² ) |
| ρ | = fluid density, kg/m³ |
Deriving the above equations used the cross-section of the orifice opening and is not as realistic as using the minimum cross-section at the vena contracta. In addition, frictional losses may not be negligible and viscosity and turbulence effects may be present. For that reason, the coefficient of discharge Cd is introduced. Methods exist for determining the coefficient of discharge as a function of the Reynolds number.[2]
The parameter
 is often referred to as the velocity of approach factor[1]
and dividing the coefficient of discharge by that parameter (as was done above)
produces the flow coefficient C. Methods
also exist for determining the flow coefficient as a function of the beta
function β and the location of the downstream
pressure sensing tap. For rough approximations, the flow coefficient may be
assumed to be between 0.60 and 0.75. For a first approximation, a flow
coefficient of 0.62 can be used as this approximates to fully developed flow.
is often referred to as the velocity of approach factor[1]
and dividing the coefficient of discharge by that parameter (as was done above)
produces the flow coefficient C. Methods
also exist for determining the flow coefficient as a function of the beta
function β and the location of the downstream
pressure sensing tap. For rough approximations, the flow coefficient may be
assumed to be between 0.60 and 0.75. For a first approximation, a flow
coefficient of 0.62 can be used as this approximates to fully developed flow.
An orifice only works well when supplied with a fully developed flow profile. This is achieved by a long upstream length (20 to 40 pipe diameters, depending on Reynolds number) or the use of a flow conditioner. Orifice plates are small and inexpensive but do not recover the pressure drop as well as a venturi nozzle does. If space permits, a venturi meter is more efficient than a flowmeter.
In general, equation (2) is applicable only for incompressible flows. It can be modified by introducing the expansion factor Y to account for the compressibility of gases.

Y is 1.0 for incompressible fluids and it can be calculated for compressible gases.[2]
The expansion factor Y, which allows for the
change in the density of an ideal gas as it expands
isentropically, is given by:[2]

For values of β less than 0.25,
β4 approaches 0 and the last bracketed
term in the above equation approaches 1. Thus, for the large majority of orifice
plate installations:

| where: | |
| Y | = Expansion factor, dimensionless |
|---|---|
| r | = P2 / P1 |
| k | = specific heat ratio (cp / cv), dimensionless |
Substituting equation (4) into the mass flow rate equation (3):
}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/5/b/b/5bbadc21368c3510e8eb3b2dd3efa328.png)
and:
}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/e/b/9/eb98a07613c583dcf396fdec180c2d96.png)
and thus, the final equation for the non-choked (i.e., sub-sonic) flow of ideal
gases through an orifice for values of β less than 0.25:
![(5)\qquad \dot{m} = C\;A_2\;\sqrt{2\;\rho_1\;P_1\;\bigg (\frac{k}{k-1}\bigg)\bigg[(P_2/P_1)^{2/k}-(P_2/P_1)^{(k+1)/k}\bigg]}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/6/e/4/6e4370c1cf9e4be0f3c2191f04b7746b.png)
Using the ideal gas law and the
compressibility factor (which corrects
for non-ideal gases), a practical equation is obtained for the non-choked flow
of real gases
through an orifice for values of β less than 0.25:[3][4][5]
![(6)\qquad \dot{m} = C\;A_2\;P_1\;\sqrt{\frac{2\;M}{Z\;R\;T_1}\bigg(\frac{k}{k-1}\bigg)\bigg[(P_2/P_1)^{2/k}-(P_2/P_1)^{(k+1)/k}\bigg]}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/1/3/7/13724d540d70b6a6fd858a35df5ad33e.png)
Remembering that
 and
and
 (ideal gas law and the compressibility factor)
(ideal gas law and the compressibility factor)
![(8)\qquad Q_1 = C\;A_2\;\sqrt{2\;\frac{Z\;R\;T_1}{M}\bigg(\frac{k}{k-1}\bigg)\bigg[(P_2/P_1)^{2/k}-(P_2/P_1)^{(k+1)/k}\bigg]}](http://upload.wikimedia.org/math/2/0/4/2045e73b0970e5b9c9e6de429212b7a5.png)
| where: | |
| k | = specific heat ratio (cp / cv), dimensionless |
|---|---|
 |
= mass flow rate at any section, kg/s |
| Q1 | = upstream real gas flow rate, m³/s |
| C | = orifice flow coefficient, dimensionless |
| A2 | = cross-sectional area of the orifice hole, m² |
| ρ1 | = upstream real gas density, kg/m³ |
| P1 | = upstream gas pressure, Pa with dimensions of kg/(m·s²) |
| P2 | = downstream pressure, Pa with dimensions of kg/(m·s²) |
| M | = the gas molecular mass, kg/mol (also known as the molecular weight) |
| R | = the Universal Gas Law Constant = 8.3145 J/(mol·K) |
| T1 | = absolute upstream gas temperature, K |
| Z | = the gas compressibility factor at P1 and T1, dimensionless |
A detailed explanation of choked and non-choked flow of gases, as well as the equation for the choked flow of gases through restriction orifices, is available at Choked flow.
The flow of real gases through thin-plate orifices never becomes fully choked. The mass flow rate through the orifice continues to increase as the downstream pressure is lowered to a perfect vacuum, though the mass flow rate increases slowly as the downstream pressure is reduced below the critical pressure.[6] "Cunningham (1951) first drew attention to the fact that choked flow will not occur across a standard, thin, square-edged orifice."[7]
For a square-edge orifice plate with flange taps[8]:
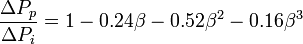
where:
And rearranging the formula near the top of this article:

Source and Terms of Use:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orifice_plate